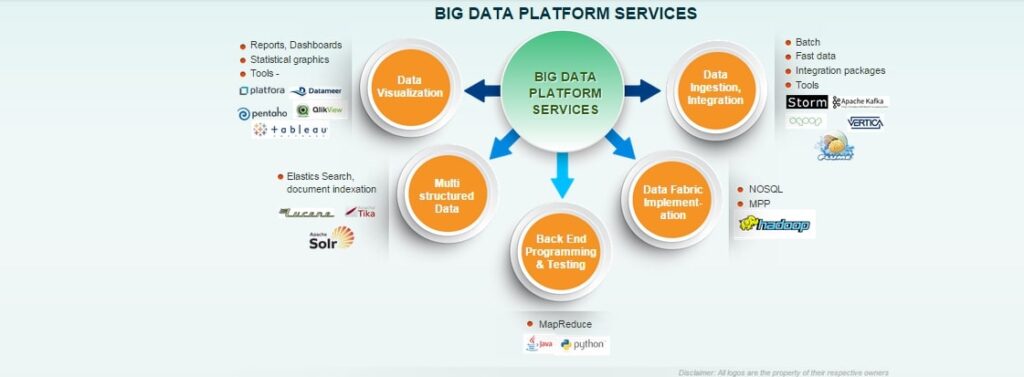
In the dynamic realm of present-day commercial enterprise, the inflow of facts has turned out to be an undertaking and a possibility. The adoption of Data Platform Services has emerged as a pivotal solution, presenting groups with a comprehensive framework for handling, studying, and deriving actionable insights from their information. This transformative method goes beyond traditional data control, providing more advantageous accessibility, scalability, and efficiency. As groups strive to navigate the complexities of the virtual age, the integration of Data Platform Services turns into a strategic vital, empowering them to unlock the real capability in their facts and thrive in surroundings in which informed choice-making is paramount.
What is a Data Platform?
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the period ‘Data Platform’ has received prominence as a complete method to the demanding situations posed by way of the exponential growth of statistics in the virtual age. A facts platform is essentially a service that acts as a relevant hub for various statistics-associated sports within an employer. It goes past mere garage and consists of functionalities for records series, processing, analysis, and visualization. In essence, a facts platform serves as the backbone of an agency’s statistics surroundings, presenting a unified and streamlined method for managing and leveraging information effectively.
Defining:
At its core, a data platform is a provider that allows the complete lifecycle of statistics, from its initial series to its eventual evaluation and presentation. Unlike traditional records control systems, an information platform is designed to be complete and adaptable, catering to the diverse needs of current groups. The number one features of a facts platform encompass:
- Data Collection: An information platform permits businesses to efficiently accumulate information from diverse assets, each internal and external, ensuring a continuous influx of statistics.
- Data Storage: Beyond just protecting data, a statistics platform provides scalable and stable garage solutions, accommodating the widespread volumes of facts generated via agencies.
- Data Processing: Transforming raw statistics into meaningful insights is a vital characteristic. Data structures appoint processing abilities to easily, rework, and structure facts for analysis.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Enabling customers to derive actionable insights from statistics is a key feature. Data systems regularly integrate equipment for analysis and visualization, empowering users to make knowledgeable selections.
Evolution of Data Platforms Inside the Business World:
The idea of facts structures has developed substantially through the years. Initially, records structures had been focused on storing and retrieving facts. However, as the significance of information in decision-making has become evident, present-day facts platforms have grown to embody a broader variety of functionalities. The evolution may be summarized in three key stages:
- Data Storage: The early days noticed the emergence of databases and garage solutions, addressing the need for a centralized region to keep and retrieve records correctly.
- Data Management: As record volumes elevated, there has been a shift closer to stronger statistics management structures that target making sure data is first-rate, governance, and compliance.
- Comprehensive Data Platforms: In the modern era, records systems have turned out to be all-encompassing, integrating functions like real-time records processing, advanced analytics, and cloud-based solutions to meet the complex demands of modern agencies.
Key Functions and Features:
A statistics platform is prominent by numerous key functions and functions that together contribute to its effectiveness in dealing with the complexities of records control:
- Unified Approach: A facts platform affords a unified method for handling the whole information lifecycle, fostering brotherly love and consistency in data-associated activities.
- Scalability: Given the ever-growing volumes of data, scalability is important. A robust information platform can seamlessly scale to accommodate multiplied facts loads without compromising performance.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that records are effortlessly reachable to legal customers across an employer is a fundamental feature. This accessibility promotes collaboration and informed choice-making.
- Security: Security is paramount inside the international facts systems. These structures implement robust safety features to safeguard touchy facts and maintain data integrity.
- Flexibility: Modern facts structures are designed to be bendy, accommodating various facts types and codecs. This flexibility ensures adaptability to the evolving information landscape.
Architecture:
A robust facts platform structure serves as the muse for green information control, processing, and evaluation inside an employer. It encompasses a cautiously designed shape of interconnected additives, each playing an essential position in making sure the seamless waft of information from ingestion to insights. In this segment, we will discover the important factors of a standard records platform structure and its capabilities.
Overview of a Typical Data Platform Architecture:
The architecture of a facts platform corresponds to the blueprint of a digital anxious machine, orchestrating the movement and processing of information. While particular implementations may vary based on organizational wishes, the subsequent additives form the core of a standard facts platform structure:
- Data Ingestion: The adventure starts with records ingestion, wherein raw records are amassed from numerous sources, together with databases, applications, sensors, and outside feeds. This thing ensures a non-stop and reliable inflow of information into the platform.
- Data Storage: Once ingested, data wishes a stable and scalable domestic environment. Data storage answers, consisting of databases, statistics lakes, or cloud-based garages, offer the infrastructure for storing massive amounts of established and unstructured records.
- Data Processing: Raw statistics regularly call for refinement earlier than they turn into insightful. Data processing involves cleaning, reworking, and structuring the information to make it suitable for evaluation. This factor makes use of diverse techniques, inclusive of batch processing and real-time stream processing.
- Data Management: Ensuring the great governance, and integrity of data falls underneath the purview of information control. This includes activities including information cleansing, metadata management, and adherence to regulatory compliance standards.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: The processed statistics are then made available for analysis. Data evaluation and visualization additives provide equipment and interfaces for customers to derive meaningful insights from the data, allowing informed choice-making.
Components in Detail:
- Data Ingestion: Collecting Data Effectively: Data ingestion is the access factor for all records into the platform. It includes choosing suitable facts sources, employing ingestion techniques which include batch or real-time processing, and ensuring statistics fine at some point in the ingestion process.
- Data Storage: Where Your Data Resides: Data garage answers ought to deal with the various desires of record endurance. Relational databases, NoSQL databases, facts warehouses, and facts lakes are not unusual garage options, every serving particular use cases based totally on records type, volume, and get right of entry to styles.
- Data Processing: Transforming Raw Data into Insights: Data processing is the engine that transforms raw statistics right into a usable layout. Batch processing handles big volumes of facts in scheduled durations, whilst real-time processing affords immediate insights, making it appropriate for packages that require instantaneous remarks.
- Data Management: Ensuring Data Quality and Governance: Data control involves sports such as information profiling, statistics cleaning, and metadata control. Ensuring information is first-rate and adherence to governance standards is critical for keeping the integrity of the whole facts atmosphere.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Extracting Actionable Insights: User-friendly interfaces, commercial enterprise intelligence tools, and visualization structures empower customers to discover and analyze statistics. This issue interprets uncooked records into significant insights, facilitating decision-making across the employer.
Data Platform as a Service (DPaaS):
In the dynamic landscape of information control, agencies are increasingly turning to cloud-based solutions to cope with the challenges posed with the aid of the growing volume and complexity of records. One such transformative approach is This Platform as a Service (DPaaS), a unified answer that streamlines the whole facts lifecycle, from ingestion to analysis, on a centralized cloud-based platform. In this section, we can delve into the nuances of DPaaS, exploring its definition, benefits, use instances, and how it differs from traditional information structures.
Understanding DPaaS:
Data Platform as a Service (DPaaS) is a cloud-primarily based provider that offers corporations a complete and unified method of handling, processing, and deriving insights from their statistics. Unlike traditional on-premise answers, DPaaS leverages the scalability and flexibility of cloud infrastructure to supply a seamless and fee-powerful records control solution.
Key traits of DPaaS consist of:
- Centralized Data Hub: DPaaS serves as a centralized hub for all records-related sports, offering a unified platform wherein information can be ingested, stored, processed, and analyzed.
- Cloud-Based Infrastructure: DPaaS leverages cloud computing infrastructure, permitting companies to scale assets based totally on call for, and reducing the want for tremendous upfront investments in hardware and renovation.
- Unified Data Services: DPaaS integrates numerous records offerings right into a cohesive solution, encompassing facts ingestion, storage, processing, analysis, and visualization, all within a single cloud environment.
- Subscription-Based Model: DPaaS generally operates on a subscription-primarily based version, permitting agencies to pay for the services they use, making it a cost-efficient option as compared to standard information platform setups.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages:
- Scalability: DPaaS offers the scalability needed to deal with various facts masses, making sure that businesses can adapt to converting necessities without compromising performance.
- Cost-Efficiency: The pay-as-you-cross version of DPaaS removes the need for large upfront investments, making it a fee-powerful solution for agencies of all sizes.
- Flexibility: Cloud-primarily based solutions offer flexibility in phrases of useful resource allocation, enabling companies to tailor their facts platform to unique business desires.
- Rapid Deployment: DPaaS enables speedy deployment, permitting agencies to install and begin using the platform quickly, accelerating time-to-perception.
Disadvantages:
- Dependency on Cloud Providers: Organizations’ use of DPaaS depends on the reliability and security measures of the chosen cloud carrier provider, which might also boost concerns associated with records’ privateness and availability.
- Customization Challenges: While DPaaS gives flexibility, a few groups might also discover it difficult to customize the solution to meet fantastically particular or unique necessities.
Use Cases and Applications:
DPaaS reveals applications across various industries and uses instances, proving to be a flexible solution for organizations with numerous needs. Some commonplace use instances encompass:
- Business Intelligence and Reporting: DPaaS allows the creation of sturdy business intelligence and reporting systems, permitting organizations to derive actionable insights from their facts.
- Real-Time Analytics: For applications that require actual-time analytics, inclusive of tracking and alerting structures, DPaaS allows the processing of data in actual time, imparting timely insights.
- Data Warehousing: DPaaS can serve as a cloud-primarily based information warehouse, offering a scalable and price-powerful answer for agencies requiring green storage and retrieval of big datasets.
- Predictive Analytics: Leveraging the superior analytics abilities of DPaaS, corporations can implement predictive analytics fashions to forecast trends and make knowledgeable selections.
How DPaaS Differs from Traditional Data Platforms:
The key differentiators between DPaaS and conventional information platforms lie in their structure, deployment model, and operational characteristics:
- Architecture: DPaaS is designed as a cloud-native answer, leveraging the architecture and services provided via cloud providers. In evaluation, traditional statistics platforms may also depend upon on-premise infrastructure.
- Deployment Model: DPaaS operates on a cloud-based deployment model, allowing users to get the right of entry to and manage data through the Internet. Traditional information structures are frequently deployed on-premise, requiring businesses to manage and keep their infrastructure.
- Operational Model: DPaaS follows a service-orientated operational model, with cloud vendors managing preservation, updates, and safety. Traditional facts platforms require businesses to manipulate their infrastructure, together with maintenance, security, and upgrades.
Key Components in Detail:
A well-designed information platform is a multifaceted ecosystem comprising numerous interconnected components that work in concert to allow green information control, processing, and analysis. In this section, we can delve into the important additives of a records platform in element, exploring their capabilities and importance in the normal structure.
Data Ingestion: Collecting Data Effectively:
Function:
- Data ingestion is the method of gathering and uploading uncooked records from diverse sources into the facts platform. This important issue guarantees a non-stop and dependable glide of facts, putting the degree for subsequent processing and evaluation.
Methods:
- Batch Processing: Involves collecting and processing information in predefined intervals.
- Real-Time Ingestion: Facilitates instant processing and analysis of incoming records.
Significance:
- Effective statistics ingestion unites the inspiration for accurate and well-timed insights, permitting businesses to harness the fee of both historical and actual-time information.
Data Storage: Where Your Data Resides:
Function:
- Data garage includes housing the ingested facts securely and successfully. The choice of garage answer relies upon factors along with information volume, type, and entry to styles.
Types of Data Storage:
- Relational Databases: Suitable for based records with nicely-defined relationships.
- NoSQL Databases: Ideal for handling unstructured and semi-based information.
- Data Warehouses: Designed for massive-scale records analysis and reporting.
- Data Lakes: Provide a flexible and scalable repository for various data sorts.
Significance:
- The right data storage answer guarantees statistics accessibility, integrity, and scalability, accommodating the varying wishes of an agency.
Data Processing: Transforming Raw Data into Insights:
Function:
- Data processing is the engine that transforms raw statistics into a layout appropriate for analysis. It includes cleansing, structuring, and organizing information to extract significant insights.
Techniques:
- Batch Processing: Handling large volumes of facts in scheduled durations.
- Real-Time Stream Processing: Facilitating instant processing and evaluation for time-sensitive programs.
Tools:
- Data processing equipment together with Apache Spark, Apache Flink, and Hadoop.
- Significance:
- Data processing guarantees that the statistics are delicate and prepared for analysis, enhancing the nice and relevance of the insights derived.
Data Management: Ensuring Data Quality and Governance:
Function:
- Data management encompasses activities that ensure the excellence, governance, and compliance of statistics. This consists of information cleaning, metadata management, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
Activities:
- Data Cleansing: Identifying and correcting mistakes or inconsistencies inside the information.
- Metadata Management: Maintaining metadata for effective facts governance.
- Data Governance: Establishing rules and practices to make certain information first-rate and compliant.
Significance:
- Effective statistics control is crucial for retaining the integrity of the entire data atmosphere, ensuring records are first-class, and adhering to governance requirements.
Data Analysis and Visualization: Extracting Actionable Insights:
Function:
- Data analysis and visualization components offer gear and interfaces for customers to discover, analyze, and derive actionable insights from the processed records.
Tools:
- Business Intelligence Platforms: Such as Tableau, Power BI, and Looker.
- Data Visualization Tools: Enabling the advent of charts, graphs, and dashboards.
Significance:
- User-pleasant interfaces empower stakeholders to interpret and apprehend facts, facilitating informed choice-making throughout the organization.
Data Platform Providers: Navigating the Landscape of Data Solutions:
The panorama of information platforms is rich and varied, with diverse providers supplying comprehensive answers to meet the evolving desires of corporations within the virtual age. In this segment, we can explore an outline of primary records platform vendors, each contributing specific strengths and competencies to the statistics ecosystem.
Overview of Major Data Platform Providers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
Overview:
- As a main cloud provider issuer, AWS offers a wide range of information services beneath its AWS Data and Analytics portfolio.
- Key services include Amazon Redshift for information warehousing, Amazon S3 for scalable object garage, and AWS Glue for statistics integration.
Strengths:
- Scalable and flexible cloud infrastructure.
- Extensive suite of managed facts services.
- Global presence with data centers in a couple of regions.
Microsoft Azure:
Overview:
- Azure, Microsoft’s cloud platform, offers a complete set of information offerings, known as Azure Data Services.
- Services consist of Azure Synapse Analytics (previously SQL Data Warehouse), Azure Data Lake Storage, and Azure Databricks for huge facts analytics.
Strengths:
- Integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem, consisting of SQL Server and Power BI.
- Hybrid cloud abilities for seamless integration with on-premise infrastructure.
- Robust security and compliance features.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
Overview:
- GCP gives a suite of facts analytics and garage solutions, collectively referred to as Google Cloud’s facts and analytics services.
- Key offerings consist of BigQuery for analytics, Cloud Storage for scalable object garage, and Cloud Dataflow for move and batch processing.
Strengths:
- Powerful analytics competencies with BigQuery.
- Strong emphasis on device getting to know AI through services like TensorFlow.
- Global network infrastructure for low-latency statistics gets entry to.
IBM Cloud:
Overview:
- IBM Cloud provides various information and AI services to assist organization-stage information control and analytics.
- Services include Db2 on Cloud for database control, IBM Cloud Object Storage, and Watson Studio for AI and system mastering.
Strengths:
- Enterprise-grade answers with a focal point on hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
- Robust information governance and compliance capabilities.
- Integration with IBM’s AI and cognitive computing technology.
Oracle Cloud:
Overview:
- Oracle Cloud offers a complete suite of database and information management offerings to aid businesses in their statistics tasks.
- Key offerings include Oracle Autonomous Database, Oracle Cloud Object Storage, and Oracle Analytics Cloud.
Strengths:
- Industry-main database solutions.
- Autonomous Database with self-driving, self-securing, and self-repairing abilities.
- End-to-cease cloud solutions for facts control and analytics.
Cloud-Based Solutions: A Paradigm Shift:
The shift closer to cloud-based solutions has revolutionized the facts platform landscape. Cloud providers offer scalable, on-call sources that cast off the need for corporations to put money into and manage their infrastructure. This paradigm shift brings numerous blessings:
- Scalability: Cloud structures offer the capacity to scale resources up or down based on the call, ensuring the finest performance and value efficiency.
- Flexibility: Organizations can pick from lots of services and easily adapt their facts platform to changing enterprise necessities.
- Cost-Efficiency: The pay-as-you-move version gets rid of the want for huge upfront investments, making cloud-primarily based answers fee-powerful.
- Global Reach: Cloud carriers function as information centers globally, enabling organizations to deploy records answers in proximity to their customers for low-latency entry.
Comparing Different Providers:
When choosing a statistics platform provider, organizations have to not forget factors which include pricing, functions, and industry-unique offerings. A specified assessment can help in making a knowledgeable decision based totally on unique commercial enterprise wishes:
- Pricing Models: Different providers may also offer variations in pricing models, inclusive of pay-as-you-cross, reserved times, or custom pricing based on usage.
- Feature Set: Assess the features provided by each company, together with data garage alternatives, analytics capabilities, system studying equipment, and integration possibilities.
- Industry Specialization: Some vendors may also provide industry-unique answers or compliance capabilities tailor-made to the wishes of precise sectors, which include healthcare, finance, or retail.
- Customer Support: Evaluate the extent of customer service and documentation supplied by using every provider to make certain well-timed help and a clean implementation process.
Benefits of Data Platform Services:
In the fast-paced and records-driven landscape of the ultra-modern commercial enterprise environment, the adoption of Data Platform Services brings forth a multitude of advantages for companies aiming to harness the electricity in their statistics. From more desirable accessibility to progressed choice-making, these services play a pivotal role in reworking uncooked statistics into precious insights. Let’s explore the important thing benefits that Platform Services provide:
Enhanced Data Accessibility:
Benefit:
- Data Platform Services destroy silos and provide a centralized hub for records-associated sports. This better accessibility guarantees that stakeholders throughout the corporation can get the right of entry to and utilize statistics for choice-making, fostering collaboration and a unified knowledge of statistics.
Impact:
- Empower teams across departments to leverage statistics insights.
- Facilitates a cohesive method of information-driven choice-making.
- Reduces facts silos and promotes a holistic view of organizational facts.
Scalability and Flexibility:
Benefit:
- These Platform Services are designed to address varying information masses and evolving business desires. The scalability and versatility they offer make sure that groups can adapt their platforms to accommodate growing volumes of records and converting necessities without compromising performance.
Impact:
- Enables corporations to scale sources primarily based on call for.
- Adapts to changing commercial enterprise requirements and records growth.
- Promotes agility in responding to market dynamics and operational wishes.
Cost-Efficiency:
Benefit:
- Cloud-based Data Platform Services regularly function on a pay-as-you-go model, casting off the want for large advanced investments in hardware and infrastructure. This fee-efficient method lets organizations control their budgets extra correctly and align costs with actual utilization.
Impact:
- Reduces capital expenditure on hardware and maintenance.
- Allows corporations to pay for the offerings they use.
- Provides a cost-effective answer for corporations of all sizes.
Improved Decision-Making:
Benefit:
- At the heart of Platform Services lies the capability to extract actionable insights from data. By providing gear for analysis and visualization, these services empower decision-makers with the data they want to make knowledgeable and strategic alternatives.
Impact:
- Enables records-driven choice-making throughout all degrees of the organization.
- Facilitates the identification of traits, styles, and outliers.
- Enhances the velocity and accuracy of decision-making approaches.
Security and Governance
Benefit:
- Data Platform Services prioritize safety and governance, making sure that sensitive information is covered and compliance requirements are met. Robust safety features and governance functions contribute to keeping the integrity and confidentiality of facts.
Impact:
- Mitigates risks associated with information breaches and unauthorized right of entry.
- Helps organizations adhere to regulatory compliance necessities.
- Establishes a framework for statistics governance and information first-rate guarantee.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Data Platform Services:
While the adoption of This Platform Services gives numerous advantages, corporations must navigate through a set of challenges and issues to ensure a successful implementation and the most desirable usage of these services. Understanding and addressing these demanding situations is essential for agencies aiming to harness the energy of their data efficiently. Let’s discover the important thing demanding situations and concerns:
Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
Challenge:
- Safeguarding touchy records is paramount, and businesses face challenges related to statistics breaches, unauthorized admission, and compliance with information protection guidelines.
Considerations:
- Implement strong encryption mechanisms for information at relaxation and in transit.
- Define and implement get entry to manipulate policies to restrict unauthorized get right of entry.
- Stay knowledgeable and compliant with statistics protection laws and guidelines.
Integration with Existing Systems:
Challenge:
- Integrating Data Platform Services with existing structures, in particular legacy systems, may be complicated and may cause disruptions in ongoing operations.
Considerations:
- Conduct an intensive analysis of present structures and facts resources.
- Develop a comprehensive integration method to limit disruptions.
- Consider phased implementations to manipulate the transition easily.
Data Quality and Governance:
Challenge:
- Maintaining records satisfactory and making sure adherence to governance requirements pose ongoing challenges, particularly as information volumes boom.
Considerations:
- Implement facts and fine warranty procedures, including cleansing and validation.
- Establish clear facts, governance rules, and processes.
- Regularly audit and monitor information quality to become aware of and rectify issues.
Regulatory Compliance:
Challenge:
- Data Platform Services need to follow a myriad of facts protection and privacy rules, adding complexity to information control practices.
Considerations:
- Stay informed approximately evolving records protection policies.
- Implement capabilities to audit and music statistics to get admission to compliance functions.
- Collaborate with legal experts to make certain alignment with local and industry-specific guidelines.
Cost Management and Optimization:
Challenge:
- While Data Platform Services offer price-green fashions, agencies may additionally face demanding situations in managing and optimizing charges as record volumes develop.
Considerations:
- Implement price-tracking tools for song utilization and spending.
- Optimize aid allocation primarily based on real data desires.
- Regularly assess and regulate the infrastructure to align with financial constraints.
Conclusion:
In the end, adopting Data Platform Services offers businesses the transformative possibility to harness the full potential in their facts. While offering more desirable accessibility, scalability, and value performance, challenges that include information safety, integration complexities, and expertise gaps ought to be navigated strategically. By addressing those considerations with careful planning and a commitment to ongoing versions, agencies can foster an information-pushed subculture, make knowledgeable decisions, and position themselves for success in the ever-evolving digital landscape. Embracing Data Platform Services is not merely a technological shift but a strategic vital for corporations in search of agility and competitiveness in the information-driven era.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the primary motive of Data Platform Services?
A: Data Platform Services serve as a comprehensive solution for coping with, processing, and studying facts inside an employer. They offer a centralized hub for information-associated activities, inclusive of information series, storage, processing, evaluation, and visualization. The primary purpose is to empower agencies to leverage their statistics correctly for knowledgeable decision-making and strategic insights.
Q2: How do Data Platform Services fluctuate from traditional records management structures?
A: Unlike conventional records control structures, Data Platform Services provide a unified and scalable method for managing the whole statistics lifecycle. They move past primary storage, incorporating functions for information processing, analysis, and visualization. Cloud-based Data Platform Services, mainly, provide flexibility, scalability, and price efficiency, getting rid of the want for vast advanced investments in hardware.