In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, wherein threats are continuously evolving, securing endpoints and server workloads is paramount. VMware Carbon Black Cloud™ emerges as a leading cloud-local Endpoint and workload safety platform, presenting a strong defense against cyber threats. In this manual, we will navigate through the intricacies of Carbon Black Cloud, unraveling its capabilities, advantages, and pivotal position in ensuring digital protection.
Understanding VMware Carbon Black Cloud:
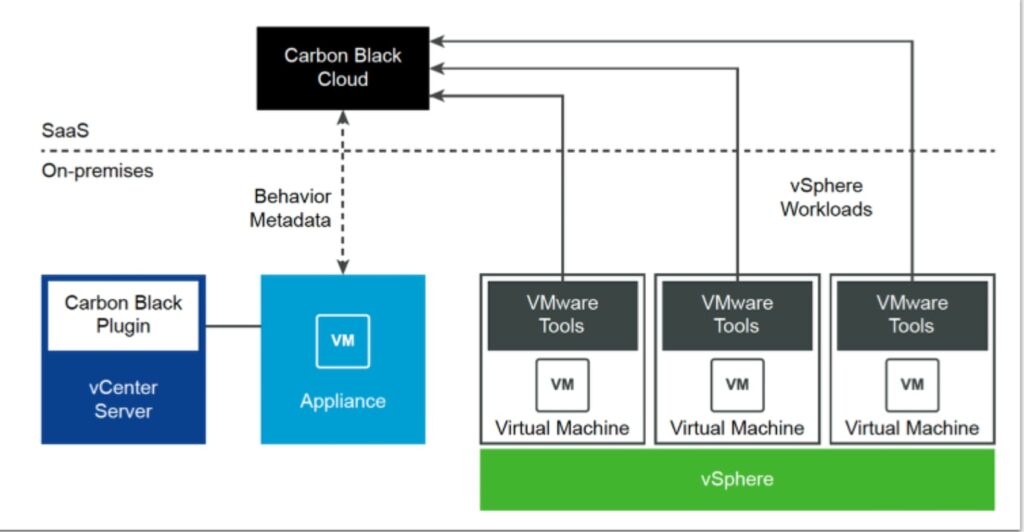
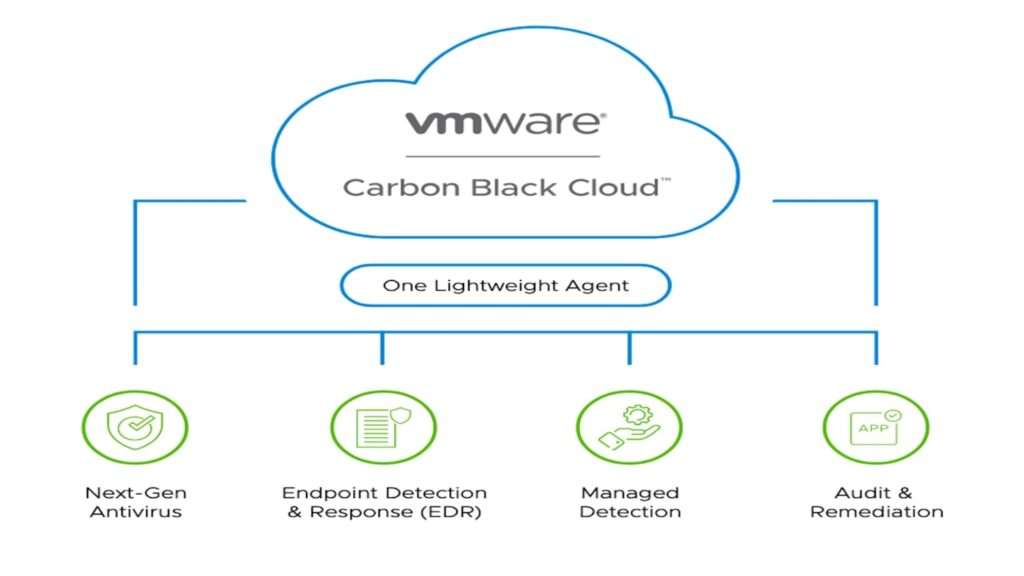
VMware Carbon Black Cloud is a current cloud-native Endpoint and Workload Protection Platform designed to safeguard agencies against cybersecurity threats. Deployed as a Software as a Service (SaaS) answer, Carbon Cloud combines next-generation antivirus (NGAV), endpoint detection and reaction (EDR), advanced hazard hunting, and vulnerability control. Its cloud-native architecture, making use of a single lightweight agent and a consumer-pleasant console, can provide comprehensive protection using behavioral prevention and smart gadget hardening. This platform empowers organizations to proactively detect, save you, and reply to cyber threats on both endpoints and server workloads, contributing to a resilient cybersecurity posture.
Cloud-Native Architecture:
Carbon Cloud’s cloud-native architecture is designed for agility and scalability, offering a dynamic and efficient security answer:
- Scalability: Adapts seamlessly to the growing digital footprint of companies.
- Flexibility: Aligns with diverse IT environments, assisting diverse cloud platforms.
- Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD): Embraces fast development and deployment practices for well-timed updates.
- Resource Efficiency: Optimizes aid usage via leveraging cloud infrastructure.
- Simplified Management: Streamlines protection operations with a centralized, user-friendly console.
This architecture ensures Carbon Cloud remains aware of evolving cybersecurity-demanding situations in modern, dynamic commercial enterprise environments.
Benefits of Cloud-Native Architecture in Carbon Black Cloud:
- Adaptation to Evolving Threats: The dynamic nature of cloud-native structure allows Carbon Cloud to adapt hastily to evolving cybersecurity threats, ensuring that businesses stay ahead of the curve.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation and scalability make contributions to operational efficiency, allowing companies to pay attention to strategic protection tasks rather than habitual duties.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud-local architectures often result in fee savings by optimizing aid utilization and averting the want for giant premature investments in infrastructure.
- Enhanced User Experience: The flexibility and scalability of Carbon Cloud’s structure contribute to a continuing and responsive consumer experience, both for security administrators and end-customers.
Importance in Cybersecurity Landscape:
Carbon Cloud holds pivotal significance within the cybersecurity landscape due to its revolutionary features and talents:
- Proactive Threat Prevention: Employs behavioral evaluation to proactively pick out and prevent rising threats.
- Real-time Detection and Response: Monitors sports in actual time, ensuring rapid detection and response to protection incidents.
- Single-Agent Efficiency: Utilizes a single, lightweight agent for seamless and efficient endpoint and workload safety.
- Comprehensive Security Services: Integrates NGAV, EDR, advanced risk hunting, and vulnerability management for holistic protection.
- Cloud-Native Agility: Adapts to the evolving danger panorama and dynamic IT environments, making sure of non-stop protection.
The platform’s multifaceted approach contributes significantly to groups’ potential to combat an extensive range of cybersecurity-demanding situations successfully.
Core Features of Carbon Cloud:
VMware Carbon Cloud integrates effective features to supply a complete endpoint and workload protection platform:
Next-Generation Anti-Virus (NGAV):
- Behavioral Analytics: Real-time monitoring for anomalous behavior.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Adaptive danger detection for recognized and unknown dangers.
- Anomaly Detection: Establishing baselines to discover deviations.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR):
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time surveillance of endpoint activities.
- Incident Analysis: In-intensity exam of security incidents.
- Automated Response: Swift responds to identified threats through automatic actions.
Advanced Threat Hunting:
- Behavioral Analysis: Proactive identification of ability threats.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Enhancing danger hunting competencies.
- Continuous Monitoring: Vigilance for emerging threats.
Vulnerability Management:
- Automated Scanning: Identification of vulnerabilities in actual time.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluation of vulnerability severity.
- Remediation Recommendations: Actionable steps for vulnerability mitigation.
Single-Agent Efficiency:
- Unified Security Agent: Lightweight, single agent for endpoint and workload protection.
- Centralized Management Console: User-pleasant interface for streamlined operations.
- Simplified Deployment: Efficient deployment across numerous endpoints.
How Carbon Black Cloud Works:
VMware Carbon Cloud operates through a dynamic combination of behavioral prevention, wise device hardening, and actual-time danger detection and reaction, ensuring a robust cybersecurity stance:
Behavioral Prevention:
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time evaluation of report and alertness behavior to locate deviations.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Adaptable algorithms identify styles associated with both acknowledged and unknown threats.
- Anomaly Detection: Establishes a baseline for everyday conduct, facilitating the identification of anomalies.
Intelligent System Hardening:
- Security Configuration Management: Ensures adherence to encouraged safety configurations.
- Patch Management: Timely application of protection patches to cope with vulnerabilities.
- Privilege Management: Limits admission to rights, decreasing the risk of unauthorized moves.
Real-time Threat Detection and Response:
- Continuous Monitoring: Monitors endpoint and workload sports in real-time for suspicious behavior.
- Incident Analysis: In-intensity analysis of security incidents to recognize their nature and scope.
- Automated Response: Utilizes automated mechanisms for rapid response to diagnosed threats.
Benefits of Using Carbon Black Cloud:
Utilizing VMware Carbon Cloud offers agencies a set of blessings, ranging from comprehensive safety to streamlined management. These advantages contribute to a resilient cybersecurity posture:
Comprehensive Protection:
- Next-Generation Anti-Virus (NGAV): Goes beyond conventional antivirus, actively identifying and neutralizing threats based on conduct.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Enhances actual-time monitoring and reaction abilities, ensuring swift detection and mitigation of protection incidents.
- Advanced Threat Hunting: Actively hunts for ability threats, proactively figuring out and neutralizing risks that may work disregarded.
Reduced Complexity with a Single Agent:
- Unified Security Agent: Utilizes a single, lightweight agent, casting off the want for more than one security answer.
- Centralized Management Console: Provides a consumer-pleasant interface for streamlined control and tracking, decreasing operational complexity.
Cloud-Native Advantage:
- Scalability: Scales seamlessly to accommodate the growing virtual footprint of agencies.
- Flexibility: Adapts to changes within the IT panorama, supporting diverse cloud environments and evolving technologies.
- Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD): Embraces CI/CD practices, ensuring rapid development and deployment of updates.
Enhanced Threat Visibility:
- Real-time Monitoring: Provides distinct insights into ability threats, allowing protection groups to detect and reply swiftly.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrates hazard intelligence feeds for the improved identity of indicators of compromise.
Proactive Security Measures:
- Threat Prevention: Proactively prevents threats via functions like behavioral analysis and shrewd device hardening.
- Vulnerability Management: Identifies, assesses, and remediates vulnerabilities, lowering the hazard of exploitation.
Carbon Black Cloud vs Traditional Security Solutions:
In comparing Carbon Cloud with conventional security answers, the important thing differences underscore the paradigm shift in endpoint and workload safety:
Cloud-Native Architecture (Carbon Cloud):
- Dynamic and Scalable: Cloud-native layout allows for dynamic scalability.
- Continuous Updates: Enables continuous integration and deployment for updated protection.
Static Infrastructure (Traditional Solutions):
- Limited Scalability: Traditional solutions can also have fixed infrastructure, limiting scalability.
- Periodic Updates: Updates and patches may be deployed much less regularly.
Scalability and Flexibility (Carbon Cloud):
- Elasticity: Dynamic allocation of assets for the most advantageous performance.
- Adaptable to Growth: Scales seamlessly with organizational expansion.
Fixed Infrastructure (Traditional Solutions):
- Static Infrastructure: May warfare successfully scale with organizational increase.
- Resource Bottlenecks: Potential useful resource bottlenecks in the course of periods of accelerated call for.
Cost-Effectiveness (Carbon Cloud):
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Eliminates large on-premise infrastructure charges.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Cloud-native version optimizes resource usage.
Infrastructure Investment (Traditional Solutions):
- High Upfront Costs: Traditional solutions might also require substantial upfront funding.
- Operational Expenses: Maintenance and operational costs can contribute to a better overall price of ownership.
Implementing Carbon Black Cloud:
Implementing VMware Carbon Cloud includes strategic making plans and execution for seamless integration into the cybersecurity infrastructure. Here’s a concise manual:
Conduct a Security Assessment:
- Identify cutting-edge vulnerabilities and cybersecurity gaps.
- Assess present infrastructure and define particular use instances for Carbon Cloud.
Develop an Implementation Plan:
- Define venture milestones and timelines.
- Allocate resources and set up communication channels for collaboration.
Integration with Existing Systems:
- Identify integration factors with contemporary protection answers.
- Ensure compatibility with endpoint structures and server workloads.
Deployment of Carbon Cloud Agents:
- Develop a deployment approach, considering phased rollouts.
- Utilize automation equipment for efficient agent deployment.
Configuration and Policy Settings:
- Customize safety rules for NGAV, EDR, and different use cases.
- Fine-track guidelines based on comments and performance metrics.
Training and Awareness:
- Provide education on Carbon Black Cloud functions and functionalities.
- Foster a tradition of cybersecurity consciousness in the agency.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization:
- Implement continuous tracking for real-time change detection.
- Conduct periodic security evaluations and tests.
Incident Response and Post-Incident Analysis:
- Develop and record incident response playbooks.
- Analyze incidents for classes discovered and continuous development.
Compliance and Reporting:
- Configure compliance reviews based totally on organizational requirements.
- Keep stakeholders knowledgeable through ordinary reporting.
Regular Platform Updates:
- Monitor release notes for brand-spanking new capabilities and safety updates.
- Test updates in a sandbox environment before deploying to manufacturing.
Future Trends in Endpoint Protection:
The landscape of endpoint safety is evolving swiftly, with rising tendencies shaping the future of cybersecurity:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
- Enhanced chance detection via adaptive algorithms.
- Reduced false positives and improved accuracy in figuring out malicious activities.
Zero Trust Architecture:
- Continuous verification and strict entry to controls for stronger safety.
- Adaptability to dynamic community environments and the upward push of far-flung work.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR):
- Holistic risk visibility throughout diverse safety additives.
- Efficient incident response through correlated statistics analysis.
Cloud-Native Security:
- Scalability and flexibility for dynamic IT environments.
- Centralized management through cloud-native architectures.
Zero-Day Attack Prevention:
- Advanced behavioral evaluation for figuring out and stopping 0-day exploits.
- Integration of threat intelligence to preemptively mitigate emerging threats.
Quantum-Safe Encryption:
- Future-proofing security features against advancements in quantum computing.
- Smooth transition to publish-quantum security standards.
Threat Hunting Automation:
- Increased performance in figuring out potential threats.
- Focus on superior threats through computerized recurring obligations.
Privacy-Centric Endpoint Protection:
- Data minimization and privacy-centered approaches.
- Alignment with evolving records safety guidelines.
Additional Tips:
- Engage in Continuous Learning: Stay up to date on Carbon Cloud’s evolving features and updates through official documentation and community forums. Leverage available training sources to enhance your expertise in the platform’s capabilities.
- Utilize Community Resources: Join online boards, consumer organizations, or groups associated with Carbon Black Cloud to trade insights and first-rate practices with other customers. Seek steerage and proportion studies to optimize your implementation.
- Implement a Testing Environment: Establish a sandbox or testing environment to securely evaluate new configurations, policies, and updates before deploying them in the production surroundings. Test specific scenarios to understand the platform’s behavior in numerous situations.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels: Foster open communication channels among IT, security groups, and different applicable stakeholders in the course of the implementation system. Ensure that everybody is aware of the modifications, and collaborate to deal with any worries or challenges.
- Regularly Review and Update Policies: Conduct periodic reviews of security guidelines inside Carbon Cloud to align them with evolving organizational needs and industry excellent practices. Update regulations primarily based on risk intelligence and remarks from security incidents.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, VMware Carbon Black Cloud is a formidable solution within the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape. With its cloud-local architecture, revolutionary functions like Next-Generation Anti-Virus (NGAV), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and Advanced Threat Hunting, Carbon Cloud provides a comprehensive defense against cyber threats. The platform’s proactive method, leveraging behavioral prevention and wise gadget hardening, units it aside from conventional protection answers. As businesses put in force Carbon Cloud, they gain from scalability, flexibility, and a unified protection agent, streamlining operations and lowering complexity. Looking ahead, Carbon Black Cloud aligns with future tendencies, including artificial intelligence, zero-believe structure, and quantum-secure encryption, ensuring it stays at the leading edge of endpoint protection. Embracing this platform indicates a commitment to robust cybersecurity, empowering businesses to safeguard their digital assets in an increasingly dynamic and sophisticated danger panorama.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the primary reason for Carbon Black Cloud?
A1: Carbon Black Cloud is a cloud-native Endpoint and Workload Protection Platform designed to shield agencies from cybersecurity threats. It combines capabilities including Next-Generation Anti-Virus (NGAV), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Advanced Threat Hunting, and Vulnerability Management to provide complete security.
Q2: How does Carbon Cloud differ from conventional antivirus solutions?
A2: Unlike conventional antivirus solutions, Carbon Cloud employs behavioral prevention and clever system hardening further to standard signature-based total methods. It proactively identifies and prevents rising threats primarily based on behavior, imparting more adaptive and robust protection.
Q3: Can Carbon Cloud be deployed in various IT environments?
A3: Yes, Carbon Cloud is designed to be bendy and adaptable. Its cloud-native architecture permits it to scale seamlessly and assist numerous cloud environments, making it appropriate for various IT landscapes.
Q4: What are the key additives of Carbon Black Cloud’s cloud-native architecture?
A4: The cloud-local structure of Carbon Cloud includes a single, lightweight agent for endpoint protection and a consumer-friendly centralized console. It leverages the scalability and versatility of the cloud, embracing non-stop integration and deployment practices.
Q5: How does Carbon Cloud manage vulnerability control?
A5: Carbon Black Cloud includes computerized scanning to discover vulnerabilities in actual time. It conducts hazard exams to assess the severity of recognized vulnerabilities and provides remediation recommendations to mitigate capability risks.
READ MORE: ClickView: A Comprehensive Guide to Revolutionize Your Educational Experience